Psoriasis is a chronic autoimmune condition that manifests as red, scaly patches on the skin, often leading to discomfort and emotional distress. This blog explores various treatment options available for managing psoriasis, from conventional medical treatments to holistic approaches, aiming to provide comprehensive relief and improve the quality of life for those affected.
Understanding Psoriasis
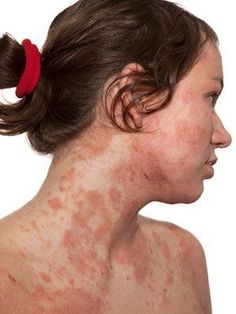
Psoriasis is characterized by the rapid growth of skin cells, resulting in thickened, red patches covered with silvery scales. These patches can appear anywhere on the body, most commonly on the elbows, knees, scalp, and lower back. The exact cause of psoriasis remains unclear, but it is believed to be related to an immune system problem with T cells and other white blood cells.
Common Triggers
Identifying and managing triggers is crucial for controlling psoriasis flare-ups. Common triggers include:
- Stress: Emotional or physical stress can worsen symptoms.
- Skin Injuries: Cuts, scrapes, sunburns, and other injuries can provoke a psoriasis outbreak.
- Infections: Streptococcal throat infections, in particular, are known to trigger guttate psoriasis.
- Certain Medications: Drugs like lithium, beta-blockers, and antimalarials can exacerbate psoriasis.
- Weather: Cold, dry weather can dry out the skin and worsen symptoms.
Conventional Medical Treatments
- Topical Treatments
- Corticosteroids: Reduce inflammation and slow skin cell turnover.
- Vitamin D Analogues: Help to slow down the growth of skin cells.
- Topical Retinoids: Promote skin cell turnover and reduce inflammation.
- Coal Tar: Reduces scaling, itching, and inflammation.
- Phototherapy
- UVB Phototherapy: Exposure to ultraviolet B light helps slow the growth of affected skin cells.
- PUVA (Psoralen plus UVA): Combines a light-sensitizing medication (psoralen) with UVA light exposure.
- Systemic Medications
- Methotrexate: Reduces skin cell production and suppresses inflammation.
- Cyclosporine: Suppresses the immune system to reduce psoriasis symptoms.
- Retinoids: Vitamin A derivatives that help to normalize skin cell growth.
- Biologics: Target specific parts of the immune system to reduce inflammation and plaque formation.
Holistic and Complementary Treatments

- Ayurveda
- Detoxification (Panchakarma): Includes therapies like Virechana (purgation) and Basti (enema) to eliminate toxins.
- Herbal Remedies: Neem, turmeric, aloe vera, and guggul help soothe the skin and reduce inflammation.
- Dietary Adjustments: Anti-inflammatory diets and avoiding triggers such as spicy foods and dairy.
- Diet and Nutrition
- Anti-inflammatory Diet: Includes foods rich in omega-3 fatty acids, fruits, vegetables, and whole grains.
- Supplements: Fish oil, vitamin D, and probiotics can support overall skin health.
- Lifestyle Adjustments
- Moisturizing Regularly: Keeps skin hydrated to reduce dryness and scaling.
- Stress Management: Techniques like yoga, meditation, and deep breathing exercises help reduce stress.
- Regular Exercise: Maintains overall health and reduces stress, which can trigger psoriasis flare-ups.
Building a Support Network
Living with psoriasis can be challenging, both physically and emotionally. Building a support network can provide comfort and practical advice:
- Support Groups: Joining local or online support groups can connect you with others who understand your experience.
- Educating Loved Ones: Informing family and friends about psoriasis can foster understanding and reduce stigma.
Conclusion
Psoriasis management requires a multi-faceted approach that includes medical treatments, lifestyle changes, and emotional support. By understanding the condition and exploring various treatment options, individuals can find effective ways to manage their symptoms and improve their quality of life. Always consult with healthcare professionals to develop a personalized treatment plan that suits your specific needs.


